Ultrasound Greenville, SC
What is an Ultrasound?
Diagnostic ultrasound (also known as sonography or ultrasonography) is a non-invasive technique used to image the interior of the body. Probes, called transducers, produce sound waves above the ability of the human ear to hear.
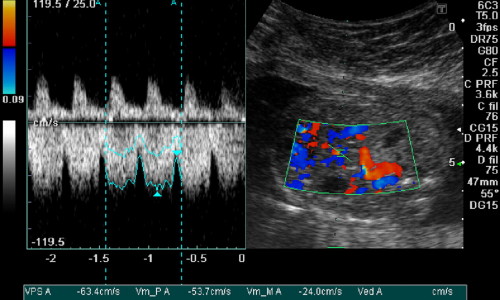
Diagnostic ultrasound can be further sub-divided into anatomical and functional ultrasound. Anatomical ultrasound produces images of the internal organs or other structures. Functional ultrasound combines information such as the movement and velocity of tissue or blood, softness or hardness of tissue, and other physical characteristics with anatomical images to create “information maps”. These maps help doctors visualize changes/differences in function within a structure or organ.
Here at EmergencyMD, we perform various high quality ultrasounds.

Ultrasound Characteristics
How Ultrasounds Work
Sound waves are produced by a transducer (a hand-held probe), which can both emit ultrasound waves, as well as to detect the echoes reflected back. In most cases, the active elements in ultrasound transducers are made of special ceramic crystal materials called piezoelectrics. These materials are able to produce sound waves when an electric current passes through them, but can also work in reverse, producing electricity when a sound wave hits them. When used in an ultrasound scanner, the transducer sends out a directed beam of sound waves into the body, and the sound waves are reflected back to the transducer from the tissues and organs in the path of the beam. When these echoes hit the transducer, they generate electrical signals that the ultrasound scanner converts into images of the tissues and organs.
Ultrasound Exams
What is an Ultrasound Used For?
Diagnostic ultrasound. Diagnostic ultrasound is able to quickly and painlessly look at internal organs within the body. However, it is not good for imaging bones or any tissues that contain air, like the lungs. Under some conditions, ultrasound can image bones (such as in a fetus or in small babies) or the lungs, when they are filled or partially filled with fluid.
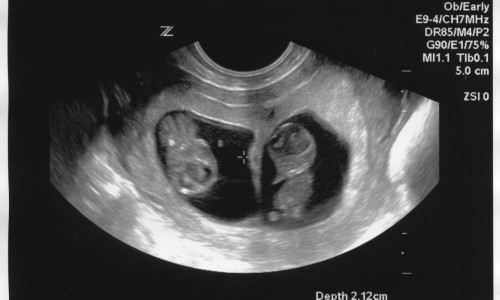
One of the most common uses of ultrasound is during pregnancy, to monitor the growth and development of the fetus, but there are many other uses, including imaging the heart, blood vessels, eyes, thyroid, brain, breast, abdominal organs, skin, and muscles. Ultrasound images are displayed in either 2D, 3D, or 4D (which is 3D in motion).